PortaFab specializes in the turn-key design and construction of modular cleanrooms including applications specifically requiring USP 797 compliance. Our in-house team of engineers, architects and designers will provide assistance with the design and qualification process, while our nationwide network of local distributors will complete the construction and installation of your new enclosure.
What is USP 797?
A Regulation and Set of Standards
USP 797 is a far-reaching regulation that applies to health care institutions, pharmacies, physician’s practice facilities, and other facilities in which compound sterile preparations are prepared, stored, and dispensed.
The purpose of the regulation is to prevent infections in patients using pharmaceutical products, as well as to protect pharmacy staff members that are ordinarily exposed to pharmaceutical products.

Below is a summary of the USP 797 regulation. For more information, visit the USP 797 website. Click here to download the entire ASHP Discussion Guide for Compounding Sterile Preparations.
Summary of USP 797: Pharmaceutical Labs & Sterile Compounding
Source of Base Information: Pharmacopeial Form, Volume 29 (4) July - August 2003
Effective Date: January 1, 2004
Scope: "The content of this chapter applies to health care institutions, pharmacies, physicians practice facilities and other facilities in which compounds sterile preparations are prepared, stored and dispensed."
Facilities Impacted by USP 797
- Facilities in which sterile products are prepared according to the manufacturer's labeling and where manipulations are performed during the compounding of sterile products which increase the potential for microbial contamination of the end product.
- Facilities where products are compounded using devices or ingredients which are not sterile to prepare products which must be sterilized prior to use.
- Products may be biologics, diagnostics, drugs, nutrients, or radiopharmaceuticals which include, but are not limited to, baths and soaks for live organs and tissues, implants, inhalations, injections, irrigations, metered sprays, ophthalmic and otic preparations.

Microbial Contamination Risk Levels
USP 797 Cleanrooms can be used in a variety of different applications with different contamination risk levels. Understanding the contamination risks of the environment you work in or the products you work with is integral to ensuring that your products and processes are USP 797 adherent.
Low Risk Conditions
Compounding with aseptic manipulations entirely with ISO Class 5 or better air quality using only sterile ingredients, products, compounds and devices. Examples of Low-Risk Conditions are listed below.
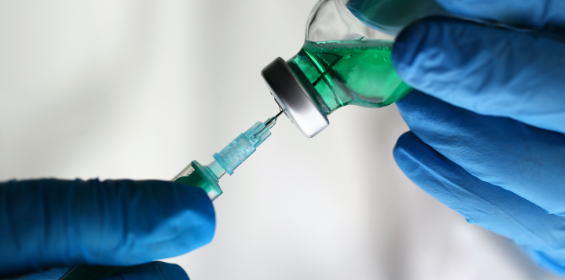
Transferring Sterile Drugs
Using sterile needles and syringes to transfer sterile drugs from the manufacturer's original packaging (vials, ampoules).

Mixing Sterile Products
Manually measuring and mixing no more than three sterile products to compound drug admixtures and nutritional solutions.
Medium Risk Conditions
Multiple individual or small doses of sterile products are compounded or pooled to prepare a compound sterile product that will be administered either to multiple patients or to one patient on multiple occasions. The compounding process includes complex aseptic manipulations other than the single volume transfer. The compounding process requires and unusually long duration, such as that required to complete dissolution or homogenous mixing. The compounded sterile products do not contain broad spectrum bacteriostatic substances and they are administered over several days. For a medium risk preparation in the absence of passing a sterility test, the storage period cannot exceed the following time periods: 30 hours at room temperature, 7 days at cold temperature, and 25 days in a solid frozen state at -20 C or colder. Examples of Medium-Risk conditions are listed below.
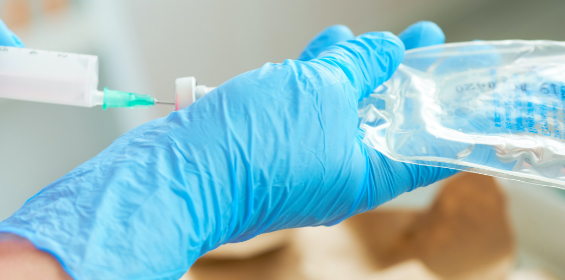
Transferring of Fluids
- TPN fluids compounded using manual or automated devices requiring multiples injections, detachments, and attachments of the nutrient source products to the device or machine to deliver all nutritional components to the final sterile container.
- Transfer of multiple ampoules or vials into a single final sterile container or products.
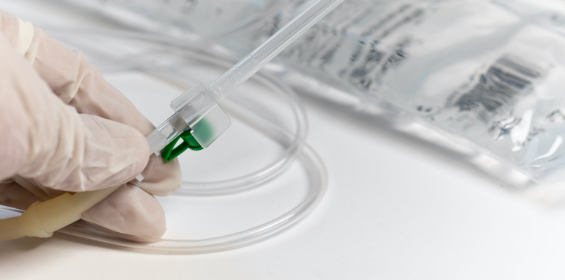
Filling of Reservoirs
- Filling of reservoirs of injection and infusion devices with volumes or sterile drug solutions that will be administered over several days at ambient temperatures between 25 and 40 degrees.
- Filling of reservoirs of injection and infusion devices with multiple sterile drug products and evacuations of air from these reservoirs before the filled device is dispensed.
High Risk Conditions
Non-sterile ingredients including manufactured products for routed of administration other than those listed under c in the in introduction are incorporated or a non-sterile device is employed before terminal sterilization. Sterile ingredients, components, devices and mixtures are exposed to air quality inferior to ISO Class 5. This includes storage in environments inferior to ISO Class 5 of opened or partially used packages or manufactured sterile products that lack antimicrobial preservatives. Non-sterile products are exposed to air quality inferior to ISO Class 5 for at least 6 hours before sterilization. For high risk preparations in the absence of passing a sterility test the storage periods cannot exceed the following; 24 hours at controlled room conditions, 3 days at cold temperatures and 45 days for solid frozen state at -20 C or colder. Examples of High-Risk Conditions are listed below.

Exposure to Inferior Air Quality
- Sterile ingredients, components, devices, and mixtures are exposed to air quality inferior to ISO Class 5. This includes storage in environment inferior to ISO Class 5 of opened or partially used packaged of manufactured sterile products that lack antimicrobial preservatives.

Mixing of Ingredients
- Dissolving non-sterile bulk drug and nutrient powders to make solution, which will be terminally sterilized.
- Measuring and mixing sterile ingredients in non-sterile devices before sterilization is preformed.
Personnel Training and Evaluation in Aseptic Manipulations Skills
Personnel who prepare compounded sterile products must be provided with appropriate training from expert personnel, audio-video instructional sources, or professional sour-ces before beginning to prepare products. Personnel shall perform didactic review, written testing, media fill testing or aseptic manipulative shills initially and at least annually for low and medium risk levels and semi annually for high risk level compounding. Media fill challenge testing will be used to access the quality of aseptic skills.
Low and Medium Risk
Buffer Area
Must have an ante area but need not be separated with a physical wall.
ISO 8+
Air classification or quality must meet ISO class 8 standards Class 100,000 (ISO 8).
ISO 14644-4 Compliant
Positive pressure to adjacent areas per ISO 14644-4.
Physical characteristics of construction
Walls, floors, fixtures and ceilings should be smooth, impervious and free of cracks, crevices and non-shedding. Surfaces should be resistant to damage from sanitizing agents. Junctures of ceilings to walls should be coved and caulked. If ceilings consist of inlaid panels, the panels should be impregnated with a polymer to render them impervious and hydrophobic and they should be caulked around each perimeter to seal them to the support frame. Walls may be panels locked together and sealed or epoxy coated gypsum board. Floors should be overlaid with side sheet vinyl flooring with heat-sealed seams and coving at the sidewall. The buffer or ante area should contain no sinks or floor drains.
Gowning
Before entering the ante or buffer area personnel should remove outer lab coats, make-up, and jewelry, and thoroughly scrub hands and arms to the elbows. After drying hands and arms they should don clean non-shedding uniforms consisting of: Hair covers, Shoe covers, Coveralls or knee length coats (coats to fit snuggly at the wrists and be zipped or snapped in the front), Appropriate gloves, Facemasks should be put on after entering the cleanroom.
Leaving and Reentry
Upon leaving the cleanroom the coveralls or coats should be carefully removed and hung outside the entry in the buffer area. Coveralls and coats can be used for one shift. All other coverings are to be discarded and new ones donned prior to reentry. Reentry follows original procedure.
High Risk
Complete Seperation
All of the low to medium risk procedures and facilities excepts the ante area must be a separate room.
A well-designed barrier isolator is an alternative to an ISO class 5 (class 100) LAFW device in an ISO class 8 clean room. The barrier isolator should be supported by adequate procedures for operation, maintenance, monitoring, and control. It is not necessary to locate the barrier isolator in an ISO class 8 area. Gowning: Hair covers, Shoe covers, Lab Coats, Facemasks (for covering facial hair).
Quality Assurance Program
For a Cleanroom to receive USP 797 Compliance it must also have a formal audit that lists all of the preparation and dispensing activities, the monitoring and evaluation procedures, specifications on the reporting of results, and other additional factors that outline that uses and activities of the area seeking USP 797 compliance.
Must have formal audit program which:
- Is formalized in writing
- Considers all aspects of preparation and dispensing
- Describes specific monitoring and evaluation activities
- Has specifications on how results are to be reported and evaluated
- Identifies appropriate follow-up mechanisms when action limits or thresholds are exceeded.
- Has delineation of the individual responsible for each aspect of the QA program.

USP 797 Guidelines - Minimum Requirements for Validation
The purpose of USP 797 is to provide standards that set the minimum threshold required for your operations to be considered safe for the preparations of compounded sterile products. Further, these standards also ensure that the compounded sterile products are of high-quality. Compounded Sterile Products include diagnostics, radiopharmaceuticals, nutrients, biologics, and drugs. Listed below are the minimum requirements for each risk category.
Low to Medium Risk
- Personnel Validation - Three consecutive media fill runs without contamination.
- Revalidation - One media fill run quarterly without contamination
- Failure of Revalidation - Three consecutive media sill runs without contamination
High Risk
- Personnel Validation - Three consecutive media fills run without contamination
- Revalidation - One media fill run quarterly without contamination
- Failure of Revalidation - Three consecutive media sill runs without contamination
- Process Validation - Three consecutive media sill runs without contamination
- Revalidation - One media fill run annually without contamination
- Failure of Revalidation - Three consecutive media sill runs without contamination

Additional USP 797 Standards
In addition to completing media fills, the workstation and area used for preparation of compounded sterile products must also pass several minimum standards before USP 797 validations can be completed. Listed below are the additional requirements.
Cleaning and Sanitizing the Workspaces
- Written procedures
- Perform at the beginning of each shift
Environmental Monitoring Required
- Verification of sterile compounding equipment
- Written plan and schedule for monitoring airborne organisms
- Verification of particulate
- Verification of viable microorganisms
Verification of automated compound devices for nutrition compounding Required
- Sterility Testing
- All high risk compounded sterile products administered by injection into vascular and central nervous systems that are prepared in groups of 25 identical or single dose packaged or in multi-dose vials for administration in multiple patients.

USP 797 - Additional Reading
Do you want to know about the additional types of cleanrooms, or the various components that can be added to ensure that your processes, products, and technicians are ISO and USP compliant? Listed below are several different links you can follow to learn more about the additional products and systems that PortaFab can offer for your cleanroom build.
Negative-Pressure Airborne Infection Isolation Rooms
Is controlling the air pressure of your USP 797 cleanroom important? Do your operations require that outside air does not enter the cleanroom, or that any volatile chemicals or microorganisms not leave the cleanroom? Read more about controlling the air pressure of your cleanroom here - Negative-Pressure Airborne Infection Isolation Rooms.
PortaFab’s Modular Cleanrooms
Modular Cleanrooms provide an excellent alternative to traditional construction methods. They are simple to install, require no cutting, create no debris, and can be relocated with ease giving your operations a degree of versatility that a permanent-non moveable construction would not be able to offer.
Cleanroom Components
Cleanroom Operations often consist of several different components working simultaneously to ensure that processes or products are protected. If your cleanroom requires additional components, PortaFab has several different solutions that you can use to enhance your build.
Cleanroom Construction Expertise
For over 30 years, PortaFab has been helping organizations with all of their cleanroom and environmental control needs. Our staff of design consultants work with architects and general contractors to deliver functional and cost-effective solutions, resulting in a smooth and quick cleanroom construction process. Read more here - Cleanroom Construction Expertise.
PortaFab’s Cleanroom Learning Center
Do you have more questions regarding cleanrooms or controlled environments? PortaFab’s Cleanroom Learning Center has several resources that can help answer your questions.

